When I first stepped into interior design, I thought I was just learning how to make spaces look beautiful. But as I transitioned into coaching, I realized something profound: the principles that create stunning, functional homes are the exact same ones that create fulfilling, intentional lives.
Think about it. Both interior design and life coaching are about transformation. Both require you to look at what’s not working, envision something better, and create a plan to get there. Most importantly, both recognize that your environment, whether physical or emotional, should support who you want to become, not hold you back.
Here’s what years of designing spaces taught me about designing a life that actually works.
Balance: The Foundation of Everything
In interior design, balance isn’t just about symmetry, it’s about creating visual harmony that feels right when you walk into a room. You might balance a heavy piece of furniture on one side with a grouping of smaller items on the other, or offset bold colors with neutral tones.
Your life needs the same kind of intentional balance.
Most people think balance means giving equal time to everything, but that’s not how it works. Just like a well-designed room doesn’t have identical furniture on both sides, a well-designed life doesn’t require identical portions of work, rest, and play.

Real balance means understanding what elements of your life need more weight and which need less. Maybe you’re in a season where career growth needs to take up more space, or perhaps family time deserves the spotlight. The key is being intentional about these choices instead of letting life happen to you.
Here’s what I learned: when something feels off in your life, it’s often because the balance is wrong, not because you’re doing anything fundamentally wrong. Sometimes you just need to rearrange the pieces.
Create Focal Points: What Deserves Your Attention?
Every well-designed room has a focal point, something that immediately draws your eye and anchors the space. It might be a stunning piece of art, a beautiful fireplace, or an incredible view. Everything else in the room supports and enhances that central feature.
Your life needs focal points too.
Without them, you end up scattered, trying to excel at everything simultaneously and feeling like you’re getting nowhere fast. I see this with so many of my clients, they’re talented, capable people who feel frustrated because they’re spreading their energy too thin.
The solution isn’t to do less (though sometimes it is). It’s to be clear about what deserves your focused attention right now.
Maybe your focal point is building deeper relationships. Maybe it’s launching that side business you’ve been thinking about for years. Maybe it’s finally prioritizing your health. The specific focus matters less than having one.
When you’re clear on your focal point, everything else falls into place more easily. Just like in interior design, other elements of your life can play supporting roles instead of competing for the spotlight.
Functionality Over Beauty: Does It Actually Work for You?
Here’s something that might surprise you: the most beautiful rooms often don’t photograph well, and the most Instagram-worthy spaces are sometimes terrible to actually live in.
As a designer, I learned that functionality always comes first. A gorgeous sofa that no one wants to sit on is just expensive art. A stunning kitchen that’s impossible to cook in defeats the entire purpose.
The same principle applies to your life choices.
That prestigious job that looks impressive on paper but drains your soul every day? That’s a beautiful-but-uncomfortable sofa. The packed social calendar that makes you look popular but leaves you exhausted? That’s the impractical kitchen.
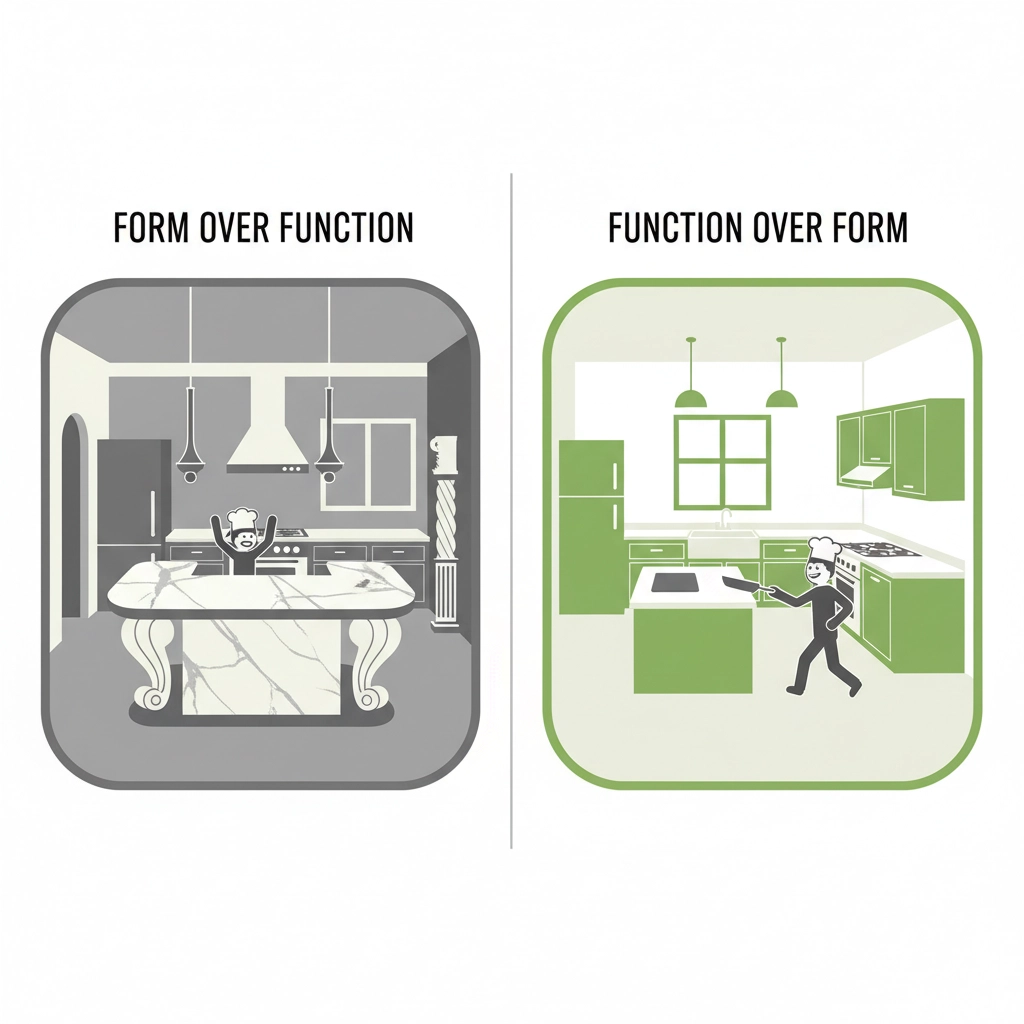
I’ve watched too many people build lives that look perfect from the outside but feel completely wrong on the inside. They choose careers, relationships, and lifestyles based on how they’ll appear to others rather than how they’ll actually function in daily life.
The antidote is asking yourself: “Does this actually work for me?” Not “Does this look good?” or “What will people think?” but “Does this support the life I want to live?”
Sometimes the most functional choice isn’t the most glamorous one. And that’s perfectly okay.
White Space: The Power of Intentional Emptiness
One of the hardest concepts for new designers to grasp is the importance of white space, the empty areas that give the eye a place to rest. Novice designers want to fill every corner, hang art on every wall, and cram in as much as possible.
But experienced designers know that empty space isn’t wasted space. It’s essential. It allows the important elements to breathe and shine.
Your life needs white space too.
In our culture of constant optimization and productivity, we’ve forgotten that rest isn’t just the absence of work, it’s an active ingredient in a well-designed life. You need time to think, to process, to simply be without agenda.
This might look like:
- Saying no to commitments that don’t align with your priorities
- Building buffer time between meetings
- Having days with no plans
- Creating physical spaces in your home that aren’t “for” anything specific
White space in your life creates room for spontaneity, creativity, and the kind of insights that only come when you’re not trying so hard.
Flow: How You Move Through Your Life
Interior designers think carefully about traffic flow: how people move through a space and whether that movement feels natural and effortless. A room might look beautiful in photos, but if you have to navigate an obstacle course to get from the couch to the kitchen, it’s not well-designed.
Your daily routines and life systems need the same kind of thoughtful flow.
Look at your typical day. Are there friction points where things consistently feel difficult or awkward? Maybe it’s your morning routine that never quite works, or the way you’ve organized your workspace, or how you transition between work and personal time.
Good flow means removing unnecessary obstacles and designing systems that work with your natural rhythms, not against them. It means being honest about how you actually function instead of forcing yourself into systems that sound good in theory.
As designer Charles Eames once said, “The details are not details. They make the design.” The small adjustments you make to improve your daily flow can have a massive impact on how your entire life feels.
Harmony: When Everything Works Together
The ultimate goal in interior design is harmony: when every element in a space feels like it belongs together, even if they’re different styles or from different eras. There’s a coherence that makes the whole greater than the sum of its parts.
Life harmony works the same way. It’s not about having identical, perfectly balanced areas of life. It’s about ensuring that your career, relationships, health, and personal growth all support and enhance each other rather than competing or contradicting.
This is where many people get stuck. They compartmentalize their lives so completely that different areas feel disconnected or even at odds with each other. Their work self feels completely different from their home self. Their values don’t align with their daily choices.
True harmony means living with integration: when who you are at work reflects who you are at home, when your daily actions align with your deeper values, when your various roles and responsibilities feel connected to a larger purpose.
Your Life, By Design
Here’s what I want you to remember: just like interior design, creating a fulfilling life is both an art and a skill. It requires vision, but it also requires practical knowledge and consistent effort.
You don’t have to live with a life that just “happened to you.” You can be intentional about the choices you make, the rhythms you create, and the environment you build around yourself.
Start small. Pick one area where you want to apply these principles. Maybe it’s creating better balance in your schedule, or identifying what deserves to be your focal point right now, or building in more white space.
The beautiful thing about this approach is that small changes often create ripple effects. When you start designing your life with the same intentionality you’d bring to creating a beautiful room, everything begins to work better together.
Your life is your masterpiece. Make it one that feels as good as it looks.
Ready to start designing a life that truly fits you? Let’s talk about how coaching can help you create the intentional, fulfilling life you deserve.